How to operate a drone is a question many aspiring pilots ask. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding its components and pre-flight checks to mastering flight control, capturing stunning aerial footage, and adhering to safety regulations. We’ll explore various drone models, control modes, and camera functionalities, equipping you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We’ll cover everything from basic terminology and safety procedures to advanced techniques for capturing professional-quality aerial photography and videography. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to enhance your existing skills, this comprehensive guide will provide a solid foundation for your drone piloting journey.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the function of key parts and highlights differences between common component types.
Drone Component Functions
Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s flight and functionality. Let’s explore the key components:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, hover, and move. Larger propellers generally produce more lift but may be less efficient at higher speeds.
- Motors: These convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, driving the propellers. Brushless motors are generally preferred for their efficiency, longer lifespan, and higher power output compared to brushed motors.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, this component processes sensor data and controls the motors to maintain stability and execute commands from the remote controller.
- Battery: Provides the electrical power for all drone components. LiPo (Lithium Polymer) batteries are commonly used due to their high energy density and lightweight nature. Battery life is a critical factor affecting flight time.
- GPS (Global Positioning System): Allows the drone to determine its location and maintain its position, essential for features like GPS mode and Return-to-Home (RTH).
- Camera: Captures photos and videos. Camera quality, features (like gimbal stabilization), and resolution vary greatly depending on the drone model.
Brushless vs. Brushed Motors
The choice between brushless and brushed motors significantly impacts drone performance and longevity. Brushless motors are more efficient, durable, and powerful, resulting in longer flight times and better overall performance. Brushed motors are simpler and less expensive but are less efficient and have a shorter lifespan.
Drone Model Comparison, How to operate a drone
The following table compares the specifications of three popular drone models (Note: Specifications are illustrative and may vary based on specific model variations and updates):
| Feature | Drone Model A | Drone Model B | Drone Model C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Camera Resolution | 4K | 1080p | 4K |
| Flight Time | 30 minutes | 25 minutes | 35 minutes |
| Maximum Range | 5km | 3km | 7km |
| Weight | 1kg | 0.8kg | 1.2kg |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
Thorough pre-flight checks are essential for safe and successful drone operation. These checks help identify potential problems before takeoff, preventing accidents and ensuring optimal performance.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, follow this step-by-step checklist:
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage (propellers, arms, body).
- Check battery level and ensure it is properly connected.
- Verify GPS signal strength and accuracy.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Power on the drone and controller, ensuring proper communication.
- Perform a pre-flight test (hover in place).
- Check surrounding airspace for obstacles and restrictions.
Sensor Calibration
Calibrating the drone’s sensors before each flight ensures accurate readings and stable flight. This typically involves following the manufacturer’s instructions, often involving specific movements of the drone.
Pre-Flight Procedure Flowchart

A visual representation of the pre-flight procedure would include boxes representing each step (visual inspection, battery check, GPS check, sensor calibration, communication check, pre-flight test, airspace check) with arrows indicating the sequence of actions. The flowchart should clearly show the conditional checks (e.g., if a problem is detected, it would lead to troubleshooting steps before proceeding to the next step).
Taking Off and Landing
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring the longevity of your drone. This section covers techniques for various environments and handling unexpected situations.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques
Takeoff and landing techniques vary depending on the environment. In open fields, a gentle, vertical ascent is ideal. In urban areas, account for obstacles and wind conditions. A smooth, controlled descent is essential for landing.
Handling Unexpected Situations
Strong winds can affect stability during takeoff and landing. In such situations, adjust your control inputs to counteract the wind’s force. If experiencing low battery, prioritize a safe landing immediately, avoiding maneuvers that could strain the battery further.
Takeoff and Landing Methods
Different drones may offer various takeoff and landing modes (e.g., assisted takeoff/landing, GPS-assisted landing). Understanding these modes and their limitations is vital for safe operation.
Controlling Drone Movement
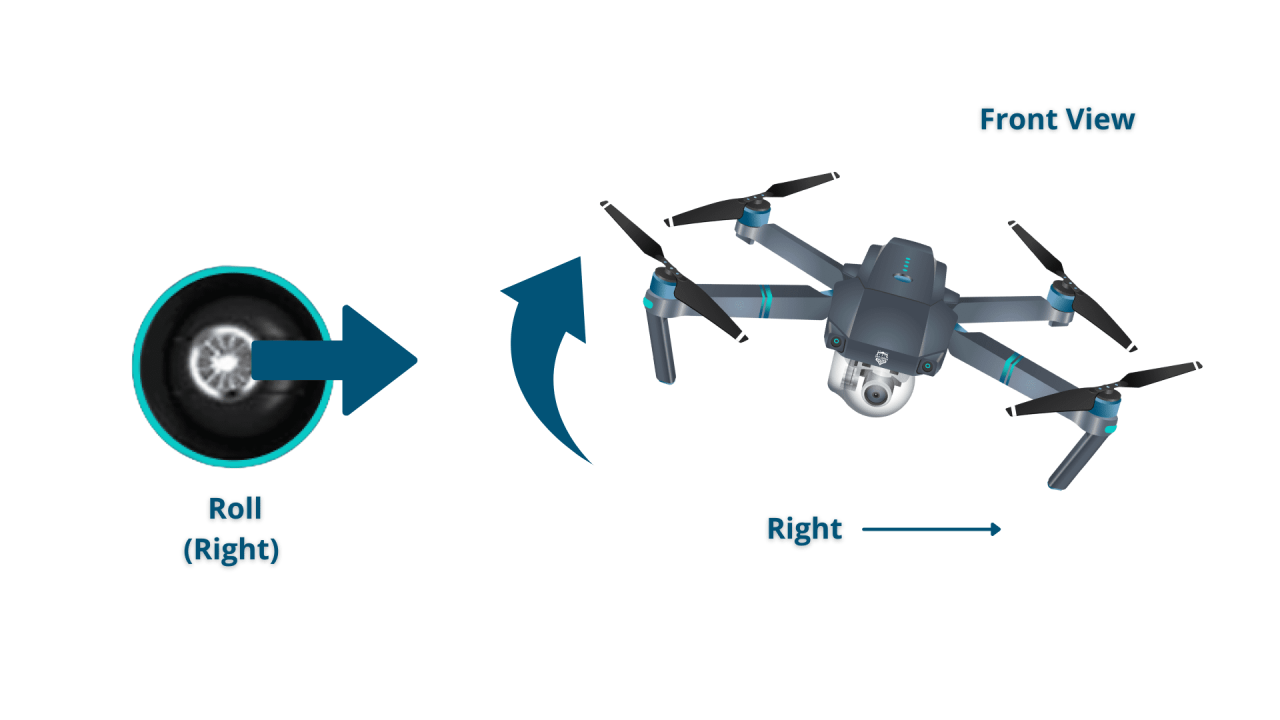
Understanding the different control modes and joystick inputs is essential for mastering drone piloting. This section explains common control modes and addresses challenges faced by beginners.
Drone Control Modes
Different control modes offer varying levels of autonomy and stability. Attitude mode provides direct control over the drone’s attitude (pitch, roll, yaw), while GPS mode allows for more precise positioning and automated functions.
Challenges for Beginners
Beginners often struggle with maintaining stable hover, controlling drone orientation, and understanding the relationship between joystick inputs and drone movement. Practice and familiarity with the controller are key to overcoming these challenges.
Joystick Inputs and Drone Actions
| Joystick Movement | Drone Action (X-axis) | Drone Action (Y-axis) | Drone Action (Rotation) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Left Stick Forward | Forward Movement | Upward Movement | N/A |
| Left Stick Backward | Backward Movement | Downward Movement | N/A |
| Left Stick Left | Leftward Movement | N/A | N/A |
| Left Stick Right | Rightward Movement | N/A | N/A |
| Right Stick Rotation | N/A | N/A | Yaw (Rotation) |
Drone Flight Planning and Navigation
Planning a safe and efficient flight path is crucial for avoiding accidents and achieving desired results. This section Artikels strategies for flight planning and navigating obstacles.
Flight Path Planning
Before flying, map out a flight path, considering obstacles, wind conditions, and legal restrictions. This ensures a smoother and safer flight.
Obstacle Navigation
When navigating obstacles, maintain a safe distance and adjust your flight path accordingly. Use features like obstacle avoidance (if available) to enhance safety.
Choosing a Flight Location
Factors to consider include airspace restrictions, proximity to people and property, weather conditions, and the presence of potential hazards.
- Airspace restrictions (no-fly zones)
- Proximity to people and property
- Weather conditions (wind, rain)
- Potential hazards (power lines, trees)
Drone Camera Operation and Photography

Mastering drone camera operation is key to capturing stunning aerial photos and videos. This section covers camera settings and techniques for high-quality image capture.
Drone Camera Settings and Features
Typical features include resolution settings, video frame rates, ISO settings, shutter speed, aperture (if adjustable), and white balance. Understanding these settings allows for customized image capture.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
To capture high-quality content, use a stable flight, consider lighting conditions, and experiment with different camera settings. Post-processing can further enhance the final product.
Adjusting Camera Settings for Different Lighting Conditions
In bright sunlight, reduce ISO and shutter speed to avoid overexposure. In low-light conditions, increase ISO but be mindful of potential noise. Adjust white balance to correct color casts.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting: How To Operate A Drone
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are essential for keeping your drone in optimal condition. This section details routine maintenance and common troubleshooting steps.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including safety procedures and legal considerations, refer to this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and enhance your skills. Ultimately, proficient drone piloting combines theoretical knowledge with practical experience.
Routine Maintenance
Regularly inspect propellers for damage, clean the drone body, and check all connections. Proper storage is also important to protect the drone from dust and moisture.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Solutions
Common issues include low battery warnings, GPS signal loss, motor malfunctions, and camera issues. Consult the manufacturer’s manual for detailed troubleshooting guides specific to your drone model.
Troubleshooting Guide
- Problem: Drone won’t power on. Solution: Check battery level and connections.
- Problem: GPS signal weak or lost. Solution: Fly in an open area with clear sky visibility.
- Problem: Motor malfunction. Solution: Inspect motors and propellers for damage; consider professional repair.
- Problem: Camera not functioning. Solution: Check camera settings and connections; try restarting the drone.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Adhering to safety guidelines and regulations is paramount for responsible drone operation. This section highlights key safety measures and legal requirements.
Safety Guidelines
Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone, avoid flying near people or property, check weather conditions before flying, and never fly under the influence of alcohol or drugs. Be aware of airspace restrictions.
Legal Requirements and Regulations
Drone regulations vary by region. Familiarize yourself with local laws and obtain necessary permits or licenses before operating your drone. These regulations often cover aspects like registration, airspace restrictions, and operational limitations.
Drone Safety Poster
A safety poster would visually depict key rules, including maintaining visual line of sight, avoiding no-fly zones, respecting privacy, and adhering to local regulations. The design would use clear icons and concise text for easy understanding. A color scheme of high contrast and clear fonts would ensure readability. The poster might include examples of unsafe practices to highlight potential hazards.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking to the skies, and a great resource to begin your journey is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This will equip you with the knowledge needed for safe and responsible drone piloting, ultimately enhancing your overall experience.
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the key aspects involved, from understanding the drone’s mechanics to navigating complex flight scenarios and adhering to safety regulations. By consistently practicing safe flying techniques and staying updated on relevant regulations, you can confidently explore the exciting world of aerial photography and videography while prioritizing safety and responsible operation.
Essential FAQs
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and autonomous features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with good flight time and ease of control.
How often should I charge my drone battery?
Charge your drone battery after each flight and avoid completely depleting it to prolong its lifespan.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
Immediately attempt to return the drone to its home point (if equipped) or initiate an emergency landing. Contact local authorities if necessary.
How do I obtain permission to fly a drone in a specific location?
Check local and national regulations for drone operation. You may need permits or authorization depending on location and flight purpose.
